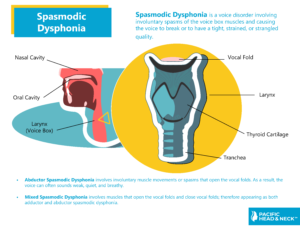
Spasmodic dysphonia is a form of dystonia, a group of neurological disorders characterized by involuntary muscle spasms. It is a voice disorder involving involuntary spasms of the voice box muscles and causing the voice to break or to have a tight, strained, or strangled quality. Patients with spasmodic dysphonia may have difficulty communicating clearly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
A diagnosis for spasmodic dysphonia may include:
- Laryngeal Electromyography (EMG):
- Laryngeal electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic exam that evaluates the health of the vocal cord muscles and the nerves that control them by measuring muscle electrical activity. This test is most commonly performed to determine the cause of muscle weakness, as well as to predict recovery from vocal cord paralysis and other related conditions. It is often performed with Botox injections to ensure that the medication is injected into the proper muscle. During the EMG exam, thin needle electrodes are inserted through the skin and into the muscle, where they detect electrical activity while the vocal cord muscle is at rest and contracting. Patients may experience mild pain when the electrodes are inserted, but this is tolerable for most. This test is usually performed in conjunction with a nerve conduction velocity test.
Symptoms
Treatment
Types of Spasmodic Dysphonia
Infographic