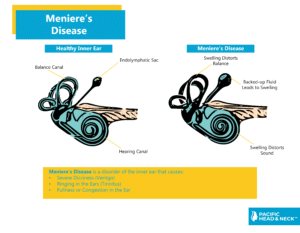
Ménière's disease (also known as endolymphatic hydrops) is the result of a fluid imbalance in the inner ear. Excessive fluid build-up can cause vertigo and affect hearing.

Diagnosis
Diagnosis
Evaluation is based on a very careful history given to the ear surgeon, as well as an examination of the ears under the operating microscope to rule out obvious infections or visible growths.
Ménière's disease is diagnosed involving physical examinations followed by tests:
- Audiometry:
- Ability to detect sounds at different pitches and distinguish between similar sounding words.
- Electonystagmography (ENG):
- Measure the nerve of balance. Over time, this nerve will lose function. Most patients with Ménière's disease have a reduced response to stimulation with cold and warm water or air which is used in this test.
- Electrocholeography (ECOG):
- This test measures the excess fluid accumulation in the inner ear and can confirm increased pressure due to the excess fluid accumulation in the inner ear.
- Videonystagmography (VNG):
- Test to evaluate where the inner ear is stimulated. The function is based on the movement of the eye.
- Complete Blood Count:
- The blood count is used to rule out any infection or weakness.
Symptoms
Causes
Treatment
Infographic